Here are my SEO predictions for 2021.
Disclaimer: All ideas are mine, and I verified all statements, but I have used GPT-3’s 175B parameter davinci model to expand my thoughts further. You will find the AI’s contributions highlighted in the text (my input in bold and its response following?).
In a nutshell:
Successful companies in 2021 will invest in interconnectedness to craft personalized digital experiences. SEO will evolve and will foster human-AI collaboration to unprecedented levels. We will see robots taking new responsibility in content marketing, technical SEO, and innovative publishing workflows.
We live in a world that we have not experienced before – COVID-19 has imposed unprecedented measures. It has significantly impacted our economy, the digital marketing landscape, and everyone’s life/work balance. This year was like no other: at current course and speed, in a few months, unemployment could reach levels not seen since the Great Depression, but at the same time, the pandemic has fueled digital transformation and the economic growth of digital services to unprecedented levels.
This blog post is also available as Web Story ? “SEO Trends 2021“
The success of WordLift, this year more than any other year, is the result of the work that we do with our amazing clients (and I cannot thank them enough for all the support and the interactions that we have). These are the trends that we will be betting on for our product’s roadmap and the success of our clients.
What are the top trends for SEO in 2021?
The trends for SEO in 2021 are related to creating easy-to-use, intuitive digital experiences across channels and devices with data and artificial intelligence. Here are the top 7 trends you need to watch in 2021:
- Natural Language Generation
- Structured Data & New SERP Features
- Passage-Based Content Optimization
- E-Commerce, everywhere
- Your Graph & Brand SERP Optimization
- Queryless search and Web Stories
- SEO Automation
Natural Language Generation is becoming an integral part of your workflow ?
Marketing is no longer the same. Machine learning and natural language processing are a natural fit for creativity, content writing, and general content optimization. 2020, much like the previous year, has witnessed one innovation after the other (from T5 to GPT-3 from PEGASUS to Turing-NLG) and an unprecedented level of improvements across the most daring NLP tasks such as content understanding, QAs answering, content generation, and more. Unlike simpler language generation approaches like the good ol’ Markov chains, which only work with a limited vocabulary, ML models using the transformer architecture can learn larger grammar and semantics patterns and re-apply them in entirely different contexts.
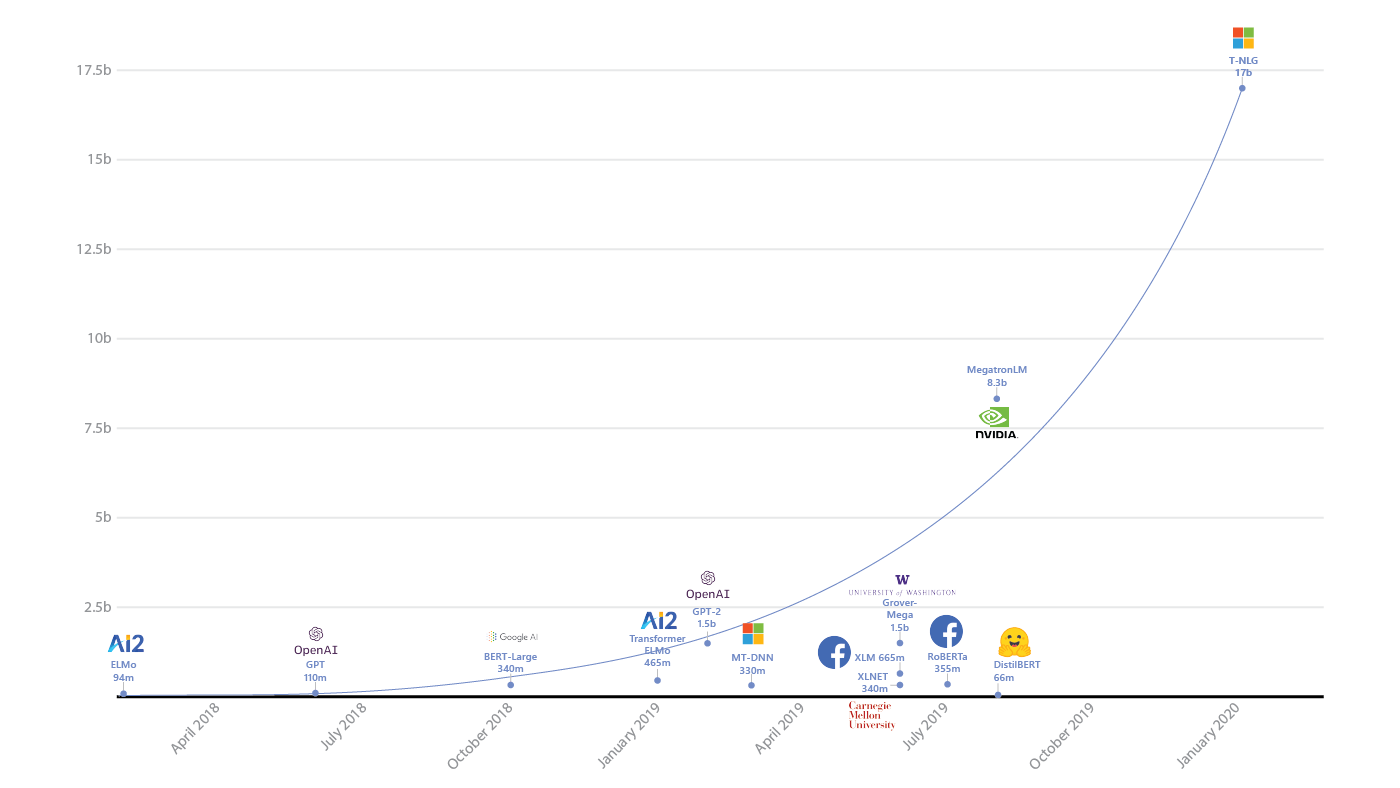
The evolution of Language Models
| Can algorithms become writers? ? Can bots become artists? The answer is yes, and the results are fascinating. My latest article for The Guardian, “Can algorithms become writers? Can bots become artists?”, explores the work of three researchers who have built algorithms to generate poetry, fiction, and music?. |
We have tirelessly worked during 2020 on the semi-automated generation of meta descriptions, story highlights (3 or 4 sentences that condense the entire article), and FAQ for hundreds of websites.
I see this trend evolving in 2021 and as I am happy to now have a simple way to summarize blog posts in WordLift, there is so much more that can be done to reduce the time spent in content research and make content easier to be found online.
Do we really need content automation? ? The main reason why you should use content automation is to save time. It’s a fact that you can’t be everywhere at once.
You can’t be writing content for all of your websites. You can’t be writing content for all of your social media profiles?.
While I don’t yet expect to have TOO MANY articles completely written by machines, in 2021, we will see AI playing a crucial role in doing the following:
?1. Gathering background information? (such as reviewing user intents, analyzing search result pages, gathering relevant news on the topic, …)
?2. Structuring the content ? (providing the outline of the article, extracting relevant questions to be answered and adding structured data markup)
?3. Writing snippets of content ? (think here about introductory text, FAQs, short summaries etc.)
?4. Reviewing the content ?(in terms of grammar and readability)
?5. Publishing the content ? (making it available to readers in multiple formats)
Indeed to quote @GaryMarcus ? pic.twitter.com/UAZc8xROEy
— Andrea Volpini (@cyberandy) December 13, 2020
Takeaway: get familiar with robot writers, make sure to plug some of this magic in your publishing workflows but remember keeping humans in the loop is still going to be essential in 2021.
2. Structured data will shape new SERP features…and a lot more
It feels like structured data will lay the foundation for the other two — so time to get comfy with those JSON brackets :-}
— ? John ? (@JohnMu) December 14, 2020
Google SERP has changed the layout, and it will continue to do so with new interactive elements that will serve the searcher way beyond what we can expect. In 2020 we have experimented with Google’s Mini Apps that provide an idea of the framework that Google uses for presenting its results to the end-user. While the experience – from the development point of view – felt similar to using Microsoft FrontPage in the nineties, the idea is clear; results are becoming (to some extent) apps.
I expect structured data to drive new rich results and provide web editors with multiple ways to interact with Google services (from Visual Search to Discover, from Google Lenses to Google Shopping). So stop focusing on TF*IDF, keyword frequency, and start building entities and your knowledge graph.
Write using the tone of Google’s John Mueller.
Structured data is so important for search engines in 2021 because ?Google is now using it as a ranking signal (not really ?)
How does Google use structured data?
Structured data is used to help Google understand what your page is about.
It’s used to help Google understand the content of your page.
It’s used to help Google understand the importance of your content.
It’s used to help Google understand the structure of your page.
It’s used to help Google understand the relationships between different pieces of content on your page?.
Using schema is vital to let search engines present your content via featured snippets and is also a way to help Google understand how the content on your site is connected (as clearly stated by GPT-3).
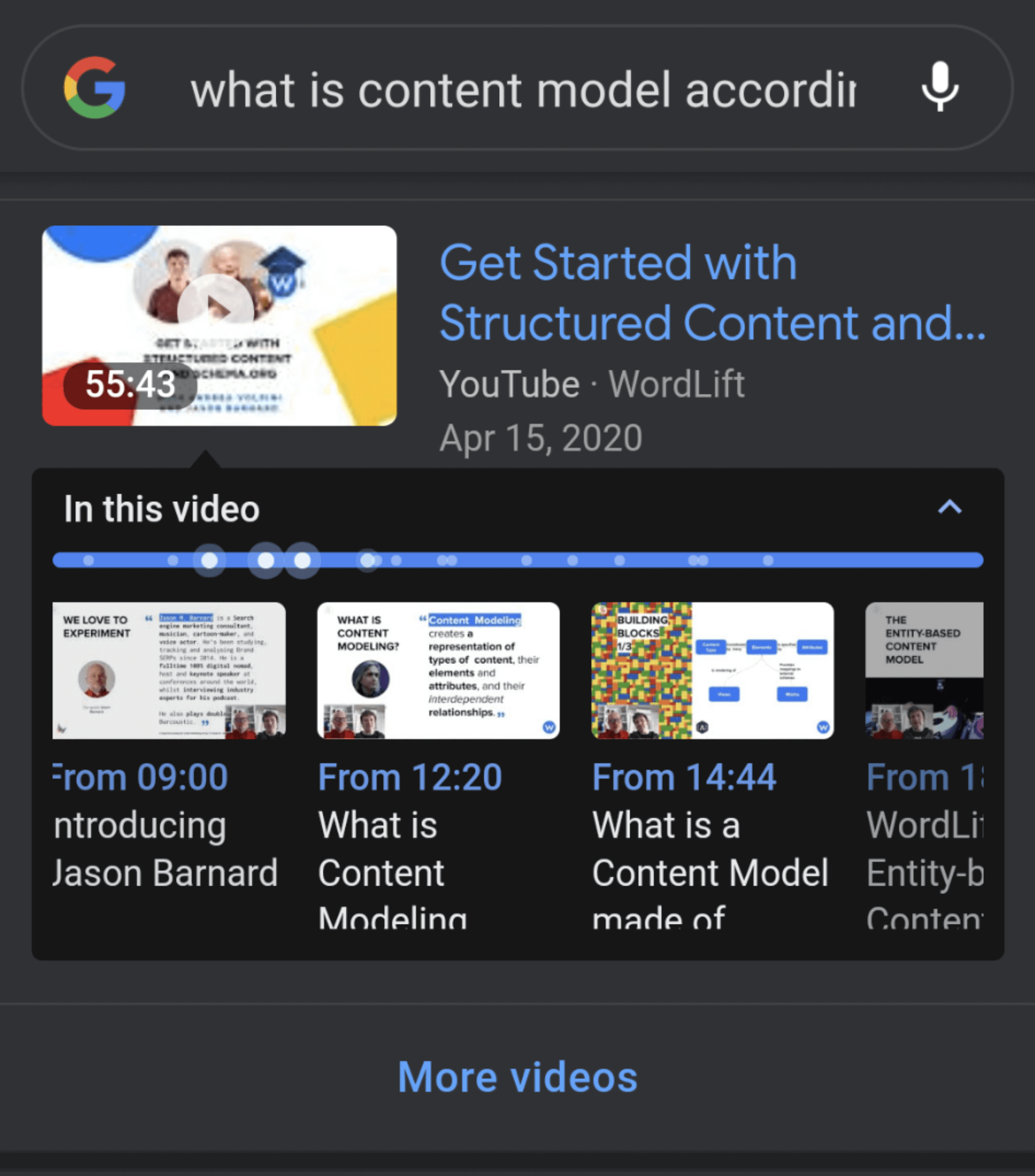
I expect to see more use-cases where structured data becomes a building block of your content strategy (check out the webinar I did with Jason Barnard on content structuring and schema markup) and a way to analyze search intents and organic traffic.
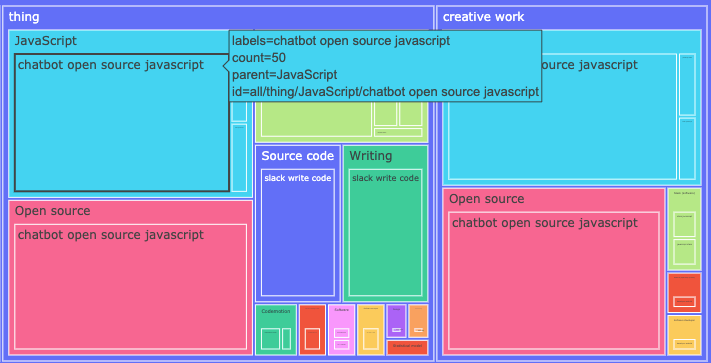
Here is a treemap of the queries extracted from the Google Search Console (for one of our clients) that we grouped using the entities in their knowledge graph. By doing so, we can more easily analyze the trends related to entity-clusters.
In the end, the more we’re capable of organizing the information architecture of our website and the more we can improve user experience and conversion rate. The page structure is becoming less relevant as users in small chunks consume information (such as PAA, Featured Snippets, and Video Clips) on Google’s SERP directly and across multiple devices. What really can connect your content with the user intent is how the content is organized and linked.
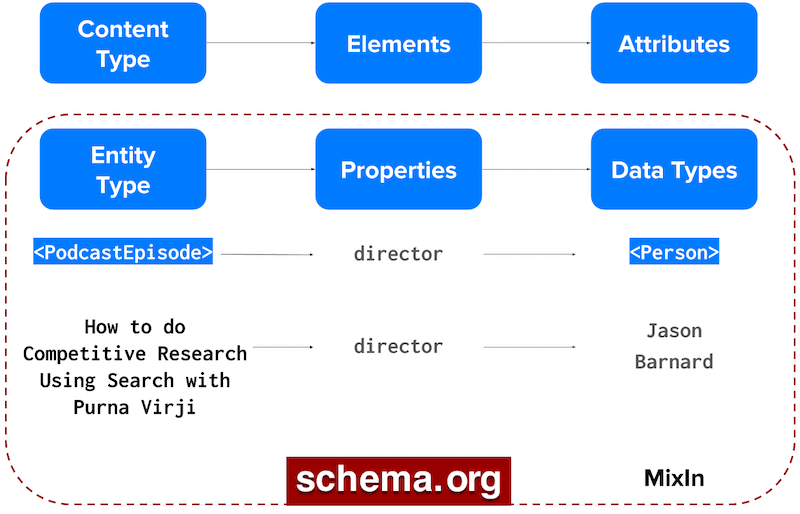
Here is the entity-based content model developed for Jason Barnard’s website using schema markup.
Takeaway: get familiar with structured data; don’t just think in terms of featured snippets but focus on the content model of your website. There is so much to gain. Remember that building your Knowledge Graph will help Google gather more insights about the entities behind your organization, your products, and your services.
3. Passage-based content optimization
Google is now capable of a more granular understanding of the page thanks to BERT-like language models (here is a good article on Google Passage Ranking).
As web publishers and marketers, our goal will be to structure content in such a way that it gets easier “for automated systems to understand the bit and pieces” as explained by Google’s Martin Splitt in the SEJ interview.
While Martin’s doesn’t expect specific actions to be taken by webmasters, I believe a few things genuinely help expand the queries that a page can rank for. Adding semantics and structuring content has proved effective with various content types already for many of our clients. From articles to recipes, from podcasts to products, we apply structured data markup to see an increasing number of search impressions from a broader set of queries.
Cindy Krum, CEO & Founder, MobileMoxie, talked about fraggles/passage optimization for years now (here is Cindy’s webinar on this topic). I believe that this will become an important trend for 2021.
Three years ago, with the help of Teodora Petkova we began experimenting with intertextuality and what we would call today passage optimization.

Read Teodora’s article “Crafting Texts in the Age of Fragmented Reader Experience” on our blog to get a sense of what passages are and how you could reshape your content to expand your reach.
Write using the tone of Google’s Martin Splitt. Is long-format good or bad for SEO?
?I’m not sure that I know the answer to that. I’m not sure that anyone does.
I do know that long-form content is good for SEO. But it’s not just about length. It’s about the quality of the content.
In my opinion, long-format content is good for SEO because it provides a better user experience, which in turn leads to better user engagement, which leads to more links and social share. But the quality of the content is the most important factor?.
How to optimize for passage ranking?
Here is what we learned so far:
- Add relevant FAQ for the target query and use structured data markup to highlight them
- When writing the answer, remember to keep it between 40-50 words (as it might also become a featured snippet)
- Add links in these FAQ answers; these links will maintain a healthy CTR and will be highlighted in bold when the passage is presented as a search snippet, featured snippet and in the People Also Ask
- Keep in mind that passage rank when they provide a consistent answer that can be spoken aloud
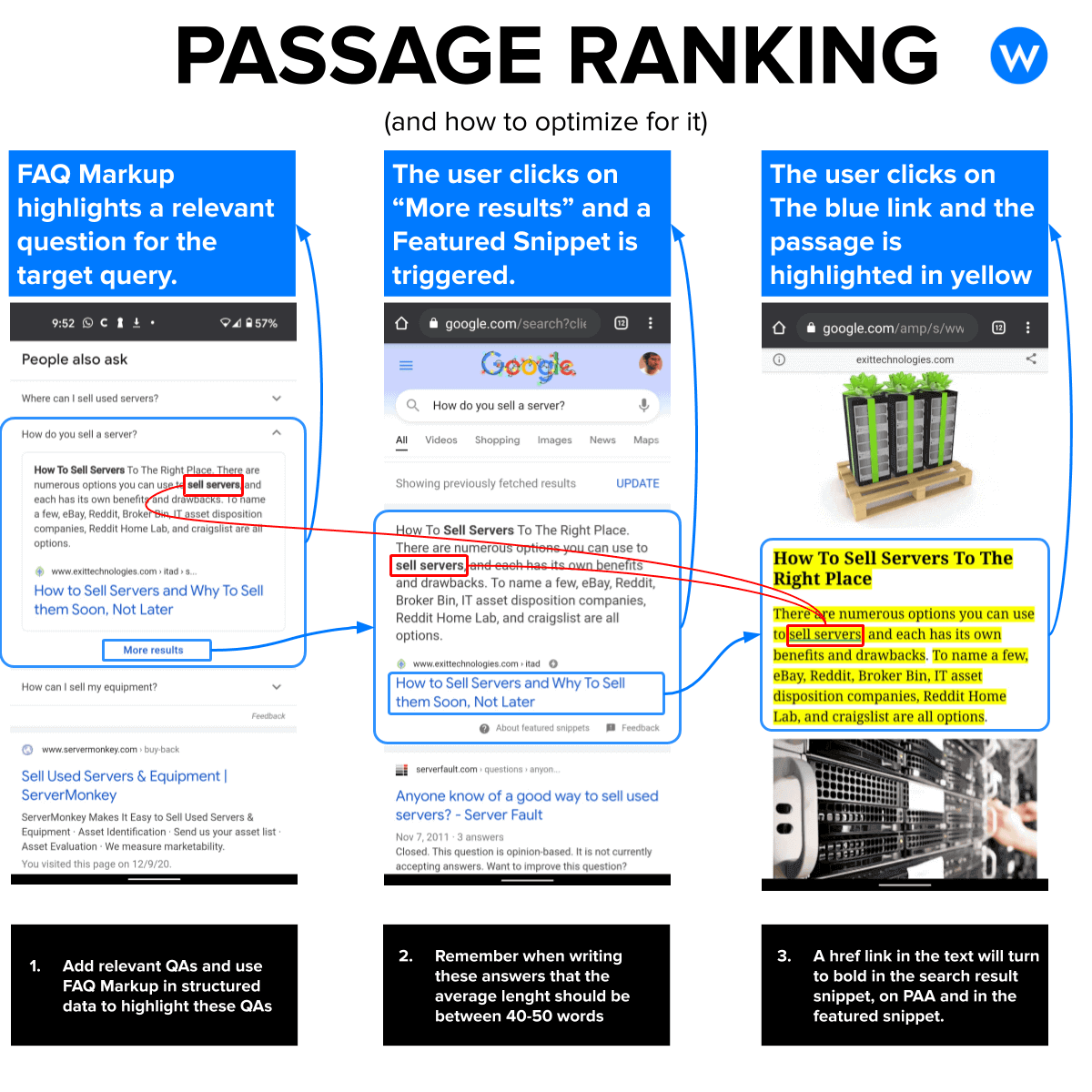
How to help Google read inside my videos?
While unrelated to what Google calls Passage Ranking, video content is also becoming more accessible. It can now be divided into chunks that have – much like passages do – their ranking opportunity in Google Search.
Video Key Moments on Google Search
This feature that now works only for English videos hosted on YouTube when we provide the timestamp information within the video description will also become available outside of YouTube and thanks to the implementation of the Clip structured data markup.
Takeaway: let the content model drive more granular queries to your website. Be ready to improve headings and to create opportunities for natural jump links to chunks of content. Embrace long-form but build multiple segments out of it. Use schema markup to semantically organize your assets (articles, courses, videos, podcasts, etc.). Improve how users move internally on your website (internal links and content recommendations) and don’t forget voice queries are on the rise.
4. E-Commerce booms and makes us rethink SEO
If you asked me two years ago, E-Commerce was not a priority for our product’s roadmap. In 2020 we have intensively worked on E-Commerce with retailers from all over the world, and we released a brand new version of WordLift just for WooCommerce. It’s been a revolution on all fronts, everywhere. It was not only retail salespeople setting up virtual appointments with customers but also managers in the public sector, doctors, teachers, and accountants. All of these meetings resulted in more online purchases.
Google has brought free retail listings to the main Google Search results page and has improved its Product Knowledge Panels to help consumers get a quick snapshot of information on a specific product entity.
As big brands will continue ramping up their online efforts while offline falters, I expect every business to use E-Commerce as the driver for their digital transformation. In SEO terms, here is what we should do:
- Improve the quality of your structured data
- Focus on the search intent and implement a long-tail strategy
- Invest in Omni-channel SEO
- Prepare for Voice Commerce
1. Improve the data quality of your catalogue and use Structured Data like a Pro
The information we provide to Google using Structured Data and Google’s Merchant Feed creates concrete new sales opportunities. Google uses information about products to populate search features, such as product Knowledge Panels or Google’s mobile Popular Products carousel. Structured data is also used to create connections within the Knowledge Graph. The more information we provide about a given product, the more comprehensive its Knowledge Panel is likely to be, and the more Google can facilitate the transaction.
Use unique identifiers for all of your products to link reviews, videos, accessories, and other elements that might be scattered across different pages of your website. In other words: build your product knowledge graph, let machines connect everything that matters to help you sell more.
Data quality is your new optimization strategy. Especially in E-Commerce, we see its importance. And once the data has been collected, cleaned, and enriched, it can also be shared as a product feed via Google’s Merchant or Google’s Manufacturer Center.
2. Go long-tail, understand the intent and improve conversions not traffic
As we move from informational to transactional intents, we need to be laser-focused on queries that might have low volume but a high chance of a conversion. Dive deep into search intents and make sure to aim at the transactional queries with your product and category pages. Keep the focus on the consumer and his/her own needs. Let’s do a quick example: the iconic Holbrook sunglasses by Oakley.

Here is the existing product overview from Oakley:
“Holbrook is a timeless, classic design fused with modern Oakley technology. Inspired by the screen heroes from the 1940s, 50s, and 60s, this design epitomizes the spirit of exploration and adventure. The iconic American frame design is accented by metal rivets and Oakley icons, perfect for those who seek equal parts performance and style.”
Assuming we’ll prepare a page targeting runners willing to purchase sunglasses, how should we rephrase this introductory text? Let’s ask our robot friend ?.
?Oakley makes a number of sports-and-outdoors sunglasses, and these are one of the most popular. The sunglasses are lightweight, and the lenses are polarized. The lens is also smaller than most Oakleys, which means less coverage over your face and therefore less chance of blocking your peripheral vision ?.
Not bad at all ?. Do you get the idea?
Artificial intelligence can become our online in-store sales rep that offers personalized guidance and recommendations to our customers.
3. Invest in Omni-channel SEO marketing
SEO helps you connect with the human beings that you want to reach and get them to interact with you. SEO, especially in the E-Commerce space, is about integrating the customer experience. I expect to see more 3D images and AR within search and Google’s SERP becoming a real multimedia hub for shoppers.
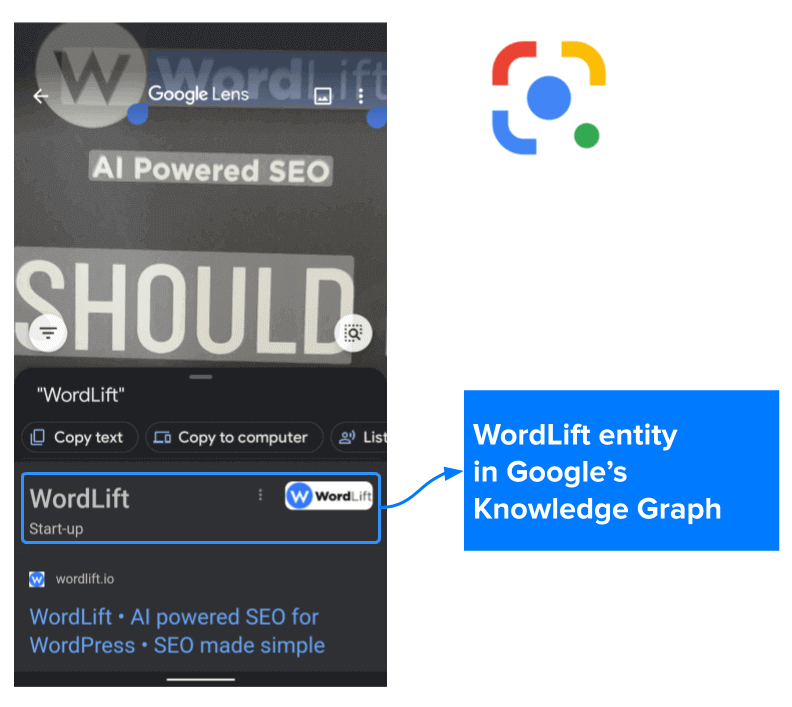
With the integration of Google Lenses, we glimpse what is happening and how you should prepare for it. Google Lenses uses visual recognition to scan things in the real world and link objects with digital experiences. Textual queries are losing ground. In some specific contexts (i.e., you are at the supermarket, choosing the right wine to buy for dinner), visual searches are already a valid alternative.
These queries – done on the spot right before the purchase – are precious: they help clients make their final decision about your product. Let’s look at an example.
Here below, I am scanning a print flyer of WordLift using Goggle Lenses. The brand is detected and reconciled with the entity in Google’s Knowledge Graph, and a link to our website is immediately available. Besides the importance of making your brand always clearly visible offline (from print materials to shop windows), there are several other aspects to consider. Images need to be very well optimized using structured data to provide Google with the necessary clues to connect the image with the entity behind it. From alt titles to EXIF / IPTC metadata, we can do a lot to link the real world with engaging new digital experiences.
4. Prepare for Voice Commerce (or V-Shopping)
According to Walker Sands one in five consumers (19%) have made a voice purchase through Amazon Echo or another digital home assistant in 2019. Another third (33 percent) planned to do so in 2020.
As people become more familiar with voice assistant devices I expect to see more Voice Commerce happening. Google Express, which is currently limited to the US only, will probably go international in 2021.

In SEO terms, preparing for Voice Commerce, means optimizing content for long-tail queries and passages. We shall optimize the top-level conversion funnel to help consumers find the answers they need around our products and services.
Takeaway: E-Commerce is driving digital transformation across all sectors. The consumer expects easy-to-use, intuitive digital experiences across channels and devices. Marketing products is about competing on customer experience. Data has become essential to link physical goods and services with digital experiences. Building a product knowledge graph is no longer an option for both big and small businesses.
5. Brand SERP optimization and Personal Knowledge Graphs
More related entities in #knowledgepanel experiments coming together…
The Yellow Koala Family are flourishing 🙂 pic.twitter.com/DzWleHG3wC
— ? Jason Barnard (@jasonmbarnard) December 10, 2020
Branding and reputation are essential in modern SEO; earning your presence in the Knowledge Graph has a tremendous impact across multiple platforms (from Google Search to Google Images, from Google Discover to Bing Search) – and requires consistency, strategy, an understanding of linked data publishing and content quality (for all your E-A-T challenges and SEO questions Lily Ray is the right person to engage with).
Creating your digital brand means cultivating, nurturing, and optimizing your Google and Bing Knowledge Graph presence. Verifying, claiming the entity, using structured data, and helping the gatekeepers (Google, Bing, Facebook, etc.) let you interact with your audience. It is also a work of consistency and data curation.
We had the opportunity, in 2020, to work side-by-side with Jason Barnard on Brand SERP optimization and the various techniques that, by leveraging Google’s Knowledge Graph, can convert visitors into customers. We will continue to focus on this track by helping users link their graphs with public graphs.
We are also live with our new data platform (codenamed WordLift Next Generation) ??. WordLift NG is bringing support for GraphQL and an extensive set of data management APIs to help brands sell products and services using data marketing.
The upcoming future of digital branding is interconnectedness: this can create a unifying vision of your brand using connected data. We don’t see Google’s Knowledge Graph only, but a growing presence of graphs of all sorts that help machines understand ourselves and the physical world.
Takeaway: Creating your graph and optimizing your presence in other large graphs like Google’s Graph, Wikidata, Bing’s Graph, and other Data Commons resources is an essential element of your 2021 digital marketing strategy.
6. Queryless search and Web Stories
Google is becoming a discovery engine. More content is actively pushed to users before they make a search.
Google Discover generates a personalized set of card style content based on the topic a user is interested in. This content include articles, videos and now web stories (Google’s new multimedia rich content format).
We expect more traffic to be generated from Google’s predictive search results across various platforms.
It’s an exciting time to learn how to use Web Stories in your content workflow and how to become a predictive search expert. We have experimented with web stories for our clients through 2020.
Before Christmas, we launched our first web story about the article you are reading right now — it turned out to be the best success of the year as we experienced a whopping +504% spike in organic traffic. Learn more about what we learned and how to create an SEO-friendly web story.
Takeaway: queryless search is on the rise. To get more visibility, optimize your content for Google Discover and create web stories, that can give your website’s organic traffic a boost and grow your reach.
7. SEO Automation
In 2021 SEO Automation, powered by natural language processing and automatic text generation, will continue to evolve. While the entire SEO workflow is still way too complicated to be entirely automated, I expect to see more AI-driven workflows that will help us improve traffic and revenues.
Using deep learning in SEO allows us to interact with Google’s giant brain at a deeper level. It will also help us predict the way forward and more quickly focus on content areas where we have more chances to create an impact.
Here is an example: a new tool that we created to help our clients find new untapped query ideas.
Takeaway: SEO Automation will continue to evolve. Focus on opportunities where, with the help of deep-learning, you can create a measurable impact.
The image used in this article is a generative design by Henklamers.