How is Conversational Search Transforming SEO
Conversational search is here. Discover what it means and how to optimize your SEO strategy to win this new challenge.
Table of content:
What is Conversational Search?
Conversational search is an emerging area of research within AI that aims to provide access to digitally stored information through a conversational user interface. The goal of such systems is to effectively process a wide range of queries in natural language, with extensive dialog between the user and the system being a critical component to understanding the user’s intent and refining responses.
This innovative approach to search leverages the advancements in natural language processing and machine learning, particularly in the development of large language models (LLMs) and natural-language understanding. These technologies enable conversational search tools to comprehend complex queries, discern context, and deliver responses that are not only relevant but also conversational in nature, closely mimicking human interaction.
The rise of conversational search signifies a shift in SEO strategies, as it goes beyond the traditional reliance on specific keywords. Instead, it focuses on the intent behind the queries, allowing for a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of user needs. As a result, businesses are now looking to optimize their content not just for keywords but for topics and semantic meaning, ensuring that their information aligns with the conversational queries posed by users.
Moreover, conversational search is not limited to text-based interactions. With the integration of voice search capabilities, users can engage with systems using spoken language, making the search experience even more intuitive and accessible. This aligns with the growing trend of using virtual assistants, such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, which are becoming increasingly prevalent in everyday life.
The impact of conversational search on user experience is profound. It offers a more personalized and engaging way for users to find information, shop online, and interact with brands. For businesses, it opens up new avenues for customer engagement, allowing them to provide instant support, answer frequently asked questions, and guide users through their websites with conversational AI-driven chatbots.
As conversational search continues to evolve, it is set to redefine the landscape of search and online interactions. By harnessing the power of AI, businesses can create more dynamic, responsive, and user-centric search experiences that cater to the evolving expectations of modern consumers.
How Does Conversational Search Impact SEO?
Unlike a traditional keyword search, a conversational search system can use grammatically complex phrases and the context of previous interactions to provide more useful and comprehensive results. In layman’s terms uses longer sentences (also defined as long tail queries in SEO). It differs from voice search, which allows users to perform searches by voice input but returns answers in text, voice, or other formats that do not evoke conversation.
Currently, search is primarily transactional: users ask for something specific and search engines try to deliver it. However, this is changing rapidly and SEO is taking on an increasingly central role. Conversational AI makes it possible to provide search capabilities that can support users with more complex search patterns and needs.
Search has changed, becoming more of an open dialog between the user and the machine. User behavior has changed. A new model for the buying process has been defined. It centers on the “messy middle,” a complex space between trigger and purchase where customers are either won or lost.
“[…] there are some things we know about buying behavior. We know that what happens between the trigger and the purchase decision process is not linear. We know that there is a complicated web of touch points that varies from person to person. But what’s less clear is how shoppers process all the information and choices they discover along the way. And what’s critical, what we are trying to understand with this new study, is how that process influences the final purchase decision”
Alistair Rennie, Jonny Protheroe – July 2020 Google
As a result, SEO is also changing, and must not only help companies get found on Google and the search engines, but also provide users with the best possible experience when searching and browsing websites. Structured data and content modeling are the ideal ally to meet this challenge because it is a reusable resource. Structured data not only helps machines understand web content, but also enables them to create a new conversational channel for interacting with users.
A chatbot works like a search engine. So working and implementing SEO on the website by using structured data and building a knowledge graph also has benefits for conversational AI like the chatbot and internal search on the website. Moreover, the same content that is created to support Google ranking and visibility can be used to train an artificial intelligence to converse like a chatbot.
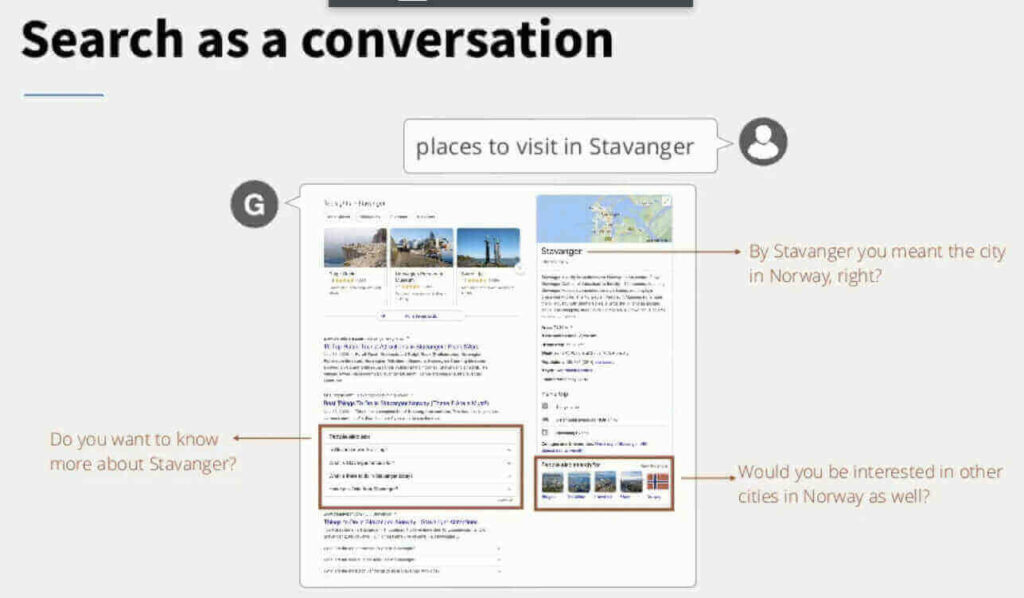
Conversational AI from an Information Retrieval Perspective: Remaining Challenges and a Case for User Simulation.
So if you create a FAQ to answer questions and get snippets highlighted on Google, you can also use this FAQ to run the chatbot on your website (and improve visitor satisfaction).
This is exactly what we did to develop the chatbot in our documentation. We trained it with the Jina AI DocsQA q-a service and enhanced its knowledge by adding FAQs (question-answer pairs) from our knowledge graph to the indexing flow. Structured data content (such as FAQPage markup) is available through WordLift’s GraphQL endpoint. In addition, we included the link to our blog to provide the user with more information about the topic and the context.
The chatbot, much like Google, to provide concise and relevant answers relies on:
- Unstructured content from our web pages (primarily the blog) and from the documentation website (we use Read the Docs for our technical documentation)
- Structured data, specifically in this case, FAQ schema markup.
Quite interestingly we can see very similar behaviors between Google and our chatbot.
Using Google
When asking “What is SEO automation?” Google will trigger (oh yeah!) a featured snippet with a text highlight pointing to the first two sentences of the blog post.
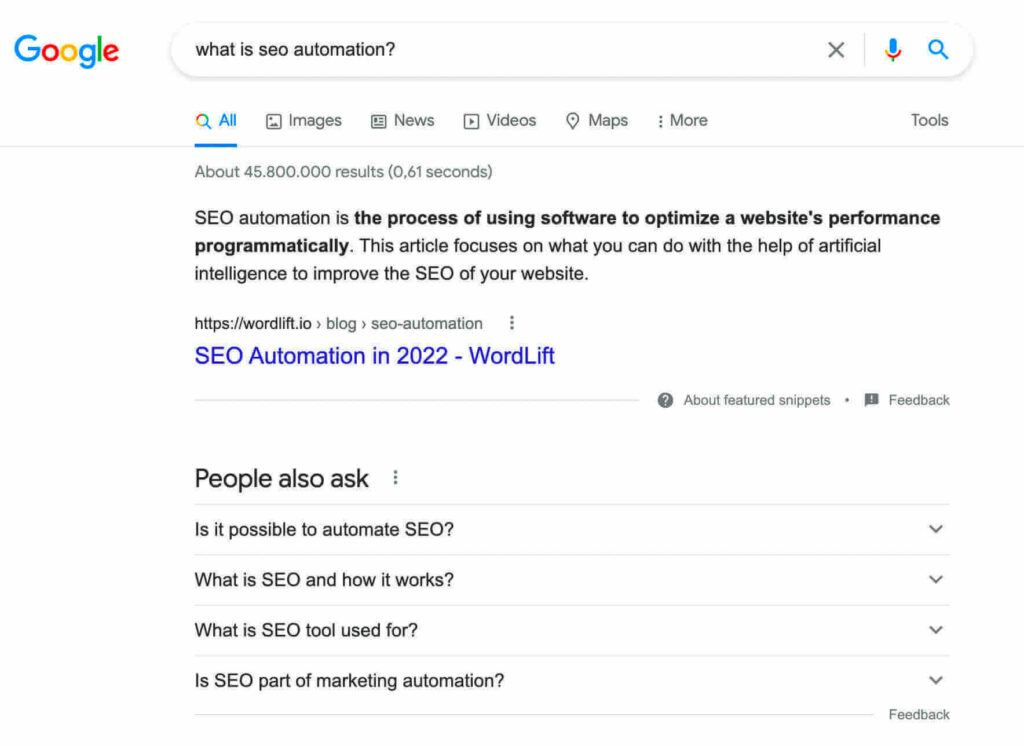
Highlight in the blogpost from Google.
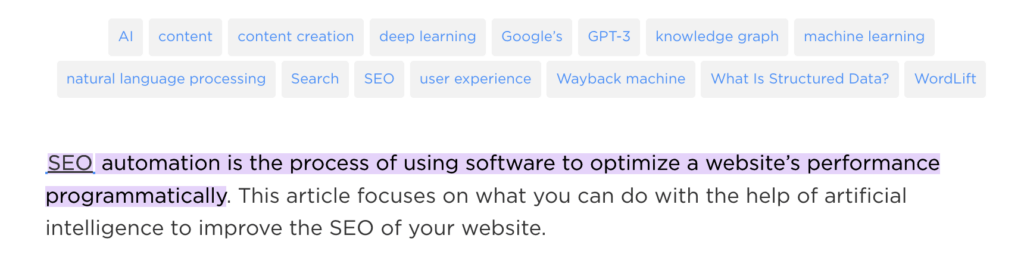
As we try to know more about SEO automation, Google might also display the result from that blog post, appearing as a FAQ snippet. See below.
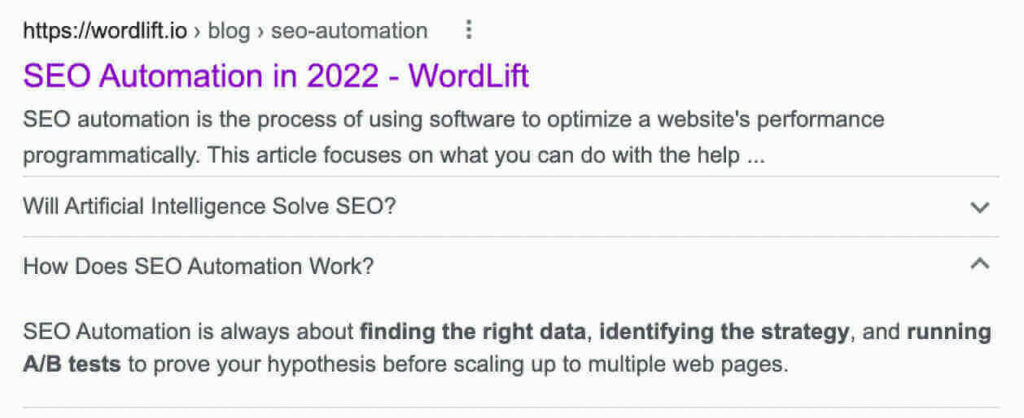
Using WordLift Chatbot
Now let’s review the same query using our chatbot. When asking “what is SEO automation?” the Jina AI-powered search engine will do exactly what Google does! It will extract the first sentence and provide, when clicking on the “See context” link an highlight (slightly shorter than the one offered by the Google’s featured snippet).
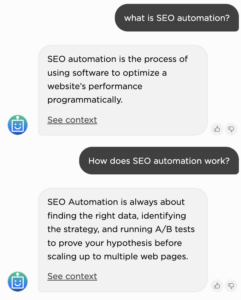
Now if we continue the conversation, and ask “how does SEO automation work?” The chatbot will use the FAQ markup behind the page. See below the related question-answer pair using the schema validator.

While Google indexes the markup available in the page as JSON-LD, the chatbot will consume the same data from the GraphQL end-point.
Highlight in the blogpost from the chatbot.
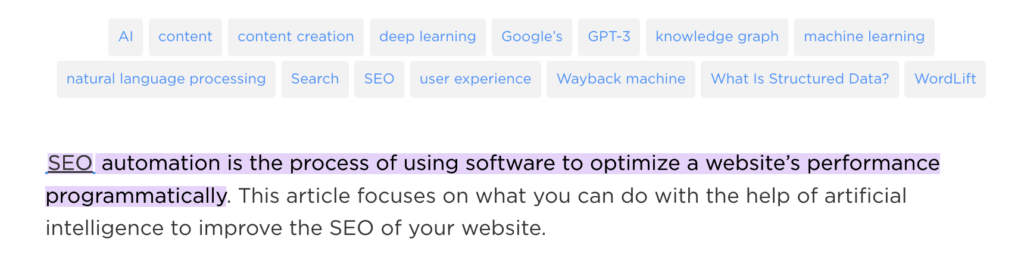
In other words WordLift is replicating what Google is doing by leveraging the same data and similar technologies (transformer-based neural networks). The scale of course is completely different.
Improved conversational search could also lead users to rely more on their virtual assistants and form an implicit “partnership” in which technology increasingly becomes a tool for exploration and problem solving, rather than just for fulfilling transactional tasks. Instead of actively searching for specific products, people may begin to use technology to better understand what they want and need.
In this way, companies can build a rich, context-based search capability that allows them to better meet users’ needs than before (and without being limited by a small number of targeted keywords). This is WordLift, the possibility for publishers to use patterns similar to those of the search engine to keep their readers engaged.
Learn more reading our article SEO And Conversational AI: A Real-World Use-Case.
Start Conversations
Conversational search enables consumers to interact more effectively with businesses through a personalized and context-based interface.
This is something that cannot be overlooked, both in SEO and in other areas, especially when it comes to developing and growing an online business.
To help businesses interact more effectively with their customers through the use of conversational AI, WordLift is exploring and experimenting with new solutions that can harness the power of conversational search.
Chatbot is an example. In WordLift we are experimenting one with the documentation space. Using AI, this chatbot can reuse data to give the user an answer to their question, but also to direct them to content on your website where they can learn more about the topic, giving them more contextual information and a better understanding of the topic.
Other Frequently Asked Questions
What is conversational AI?
Conversational AI is the set of technologies, such as virtual assistants or chatbots, that can “talk” to humans (e.g., answer questions).
Conversational AI tools use machine learning, automatic responses, and natural language processing. Their goal is to recognize and replicate speech and communication and create an experience of human interaction.
AI technology can accelerate and simplify relationships with consumers by answering their questions and relaying their requests. It can be used on websites, online stores, and social media channels, and is often used in customer service.
What can conversational AI be used for?
Conversational AI in SEO can be used to increase business by:
- Building a personalized user experience.
- Gathering data to better understand the consumer.
- Achieving more conversions and new up-sell opportunities.
What is an example of conversational AI?
A chatbot is an example of conversational AI. It works like a search engine. The same content that we prepare for Google can also be used to train an artificial intelligence for conversations like a chatbot. And that’s exactly what we did to develop the chatbot for our documentation.
We trained our chatbot with the Jina AI DocsQA q-a service and expanded its knowledge by adding FAQs (question-answer pairs) from our Knowledge Graph to the indexing flow. Structured data content (such as FAQPage markup) is available through WordLift’s GraphQL endpoint.